Major Discoveries of the Koliatsos Lab
- Axotomy responses in CNS and PNS recapitulate cytoskeletal changes in human neurodegenerative disease
- Neurotrophins and GDNF are potent survival factors for specific neuron types: NGF for central cholinergic neurons, BDNF NT4/5 and GDNF for motor neurons, BDNF for central serotonin neurons etc
- Neurotrophin transduction is dependent on binding to and phosphorylation of Trk receptors in retrogradely transported complexes
- Apoptosis is a universal mechanism of neuronal death in developmental and late-onset neurodegenerative diseases although mechanisms may differ
- Distinct classes of NOS(+) cortical interneurons are important for transsynaptic signaling of cell death in animal models of disconnection and in early Alzheimer’s disease
- Trophic signals interact with steroid hormones in ways that may be key for neuronal survival
- Neural stem cells are present in distinct niches in the adult CNS beyond the classical dentate gyrus and subventricular zone-rostral migratory stream
- Spinal cord is fully capable of processing and responding to growth signals and shows substantial repair potential after neural stem cell transplantation
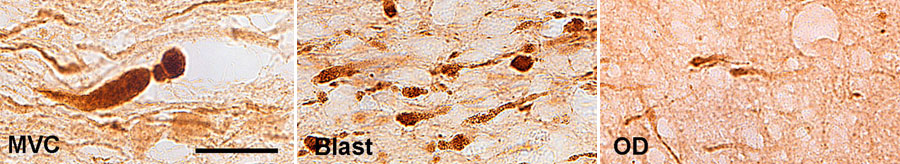
- Blast injury to brain needs to be modeled in whole animals and systemic/ vascular factors may be essential as mechanisms of injury
- Concussion can be reproduced in rodents and the visual and corticospinal tracts are excellent model systems in which to study diffuse traumatic axonal injury
- Traumatic axonal injury is the most common lesion in adult TBI including blast injury and CTE
- Mild TBI exacerbates rate and severity of tauopathy in mice predisposing to tau aggregation
- Traumatic axonal injury in the CNS initiates chronic axonopathies proceeding with Wallerian mechanisms that can be prevented or treated by interfering with DLK and SARM1 enzyme activation
- In some CNS systems, traumatic axonopathies are associated with substantial terminal field repair via collateral sprouting
Reuters.com video – August 13, 2015
Hidden Damage Revealed in Veterans’ Brains